Which heating systems are available? How is energy consumption measured? How is the energy consumption?

Abstract:
Heating systems and measuring devices differ in Germany from those in other countries. Consumption determination sometimes leads to misunderstandings.
What types of heating systems are used in Germany?
- Central heating system
- Electrical Heating
- Wood burner/open fire in chimney
Most residential buildings, especially those with multiple units, use central heating.
How is a central heating system constructed?
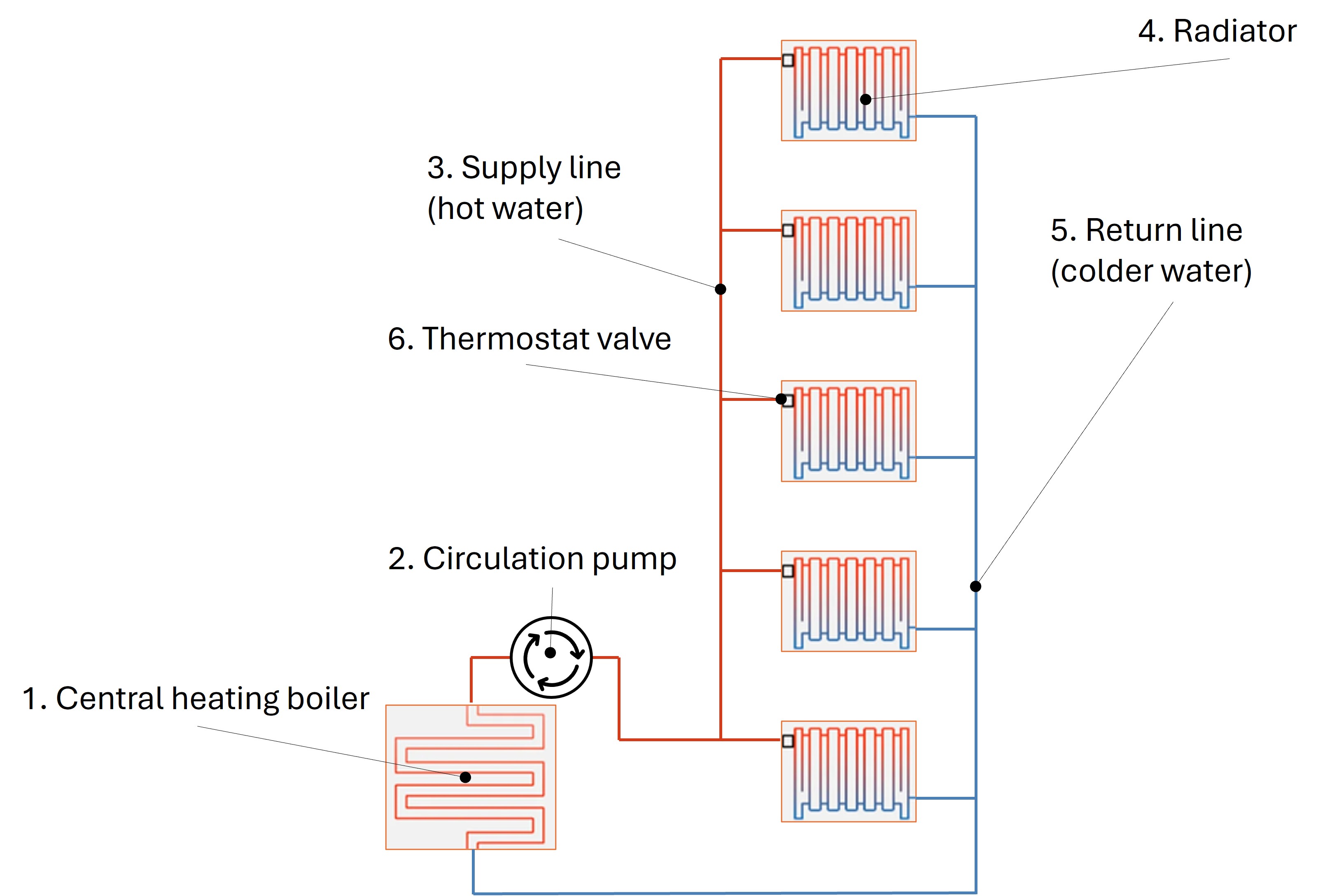
In a central heating system, water is heated in a central heat source, hence the name, and then distributed to the places of consumption. The diagram shows how in the central heating boiler (1.), with the help of the circulation pump (2),warm water is transported in the supply line (3.) and passed through radiators (4.). The amount of hot water that flows through the radiator is controlled by the thermostat valve (6.). After the heat has been transmitted to the air, the colder water, the return line (5.), is pumped back to the boiler. The process then starts again from the beginning and is therefore called "closed heating circuit".
Which types of energy are mostly used in Germany to gain thermal heating?
To generate heat, either solar energy, electrical energy, geothermal energy or, this is still the most common, heating by combustion is used.
How does the heat get from the central heating system to the points of consumption?
The hot water is pumped through pipes to the point of consumption.
In the simplest case it can be used directly there or, and this is the state of the art, transferred to the point of consumption using a heat exchanger.
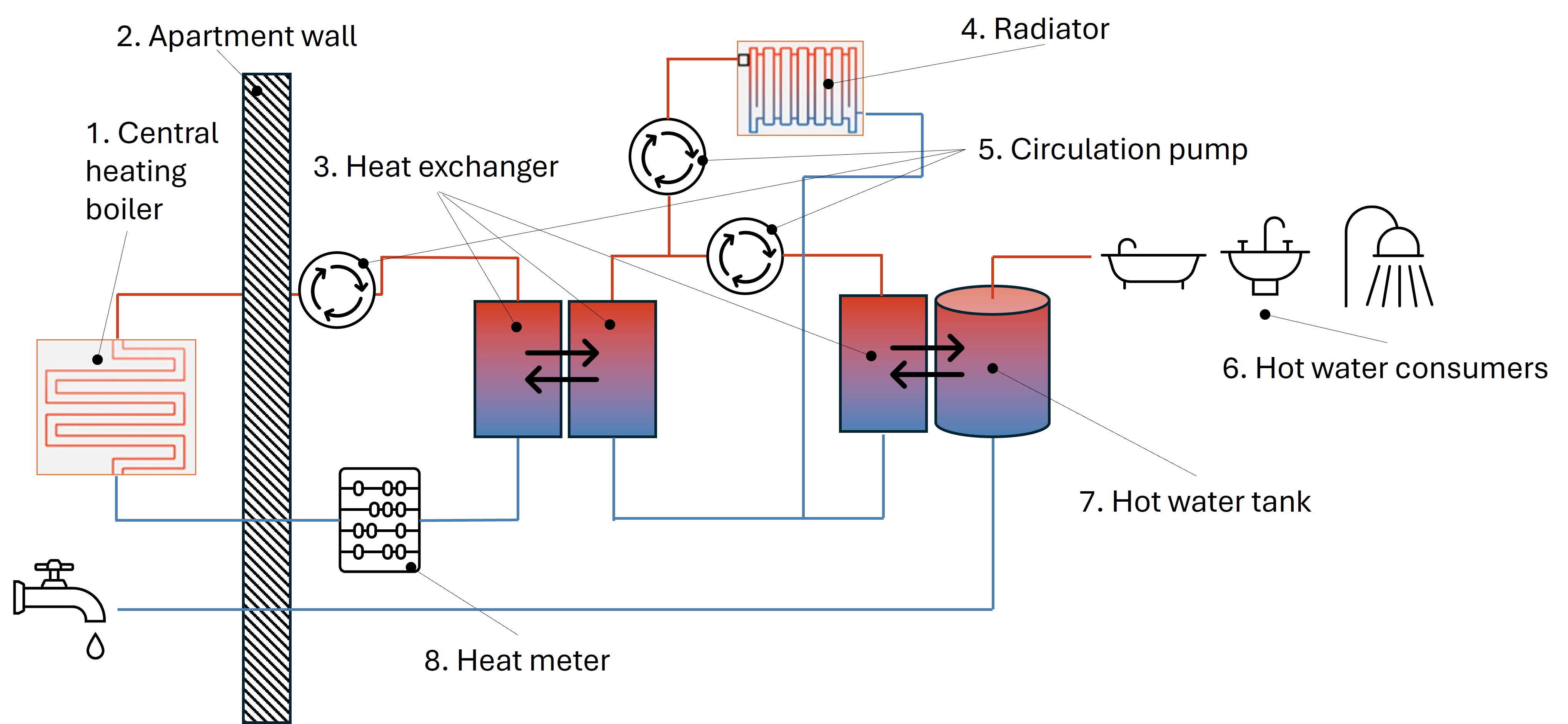
The diagram explains the circuit using heat exchangers. Hot water is generated centrally via the heat source (1.), previously explained as the "boiler". The hot water is pumped through the apartment wall (2.) via pipes. Inside the apartment there is the heat exchanger (3.). This transfers the heat to another closed heating circuit within the apartment. This heating circuit supplies the radiators (4.). It also heats the hot water for the hot water consumers (6.). A hot water tank (7.) is used for two reasons. Firstly, to save electrical energy, otherwise the circulation pump (5.) would have to run constantly. Secondly, to avoid delays as short as possible when hot water is needed by the hot water consumers (6.). Since a hot water tanks costs money and needs space, it depends on the aparment standard/space if it is realized or not.
The heat meter (8.) is a very accurate measuring device that measures the energy that has been transferred into the apartment.
Why is a heat exchanger used?
This is done for efficiency reasons.
If the hot water is used directly, it has to take a long way from the heat source to the point of consumption. In case, no hot water is needed overnight, the cold water staying in the pipe would first have to run out before warm water arrives after a longer period of time.
For this reason, a modern heating system is divided into several closed heating circuits, see diagram above. The circuits are connected to each other by heat exchangers. The closer the heat exchanger or hot water tank is located to the point of consumption, the less cold water has to flow out before warm water arrives.
How many heat exchangers are used in a house?
In the simplest case, and this was standard until the 1980s, a heat exchanger is used between the hot water production circuit and the hot water usage circuit.
In modern heating systems, the circuits are reduced in size for the reasons mentioned above, so that in an apartment building each apartment has its own heat exchanger.
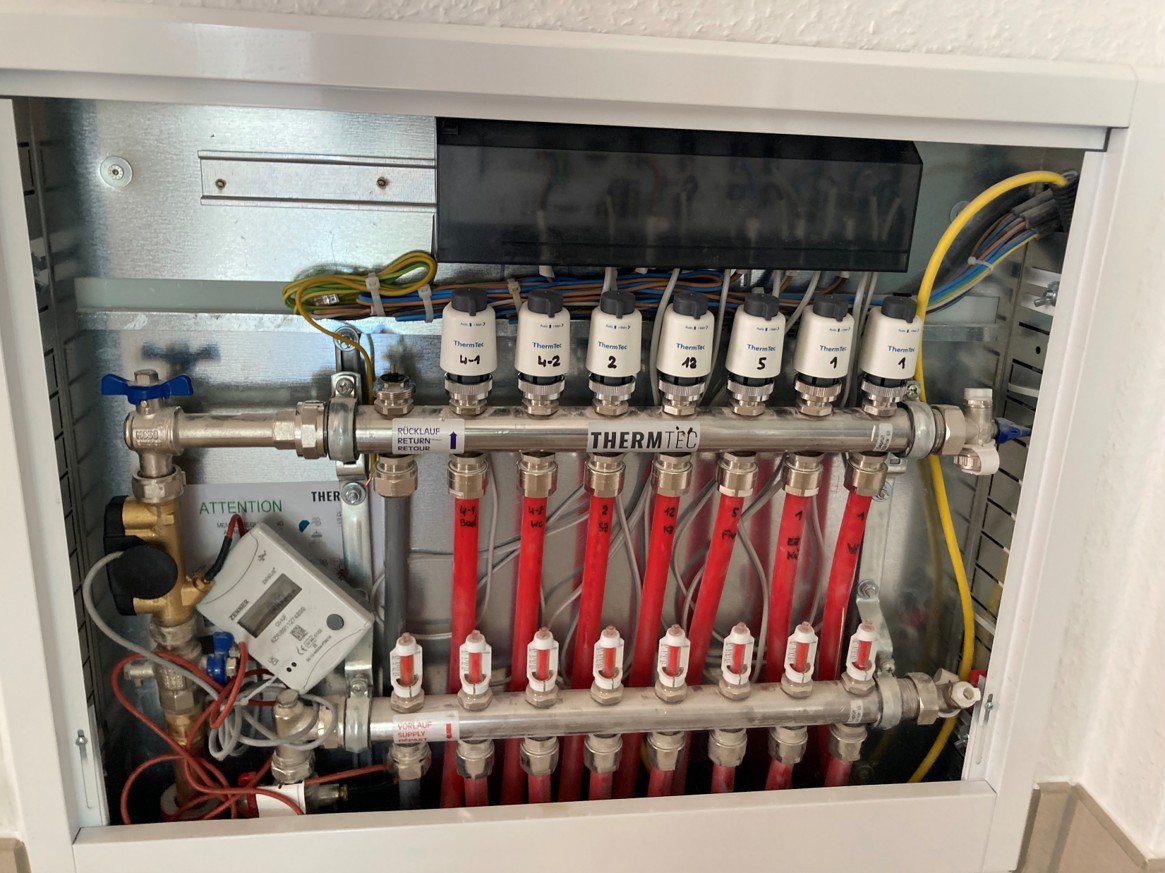
In the picture you can see a heat exchanger combined with a distributor for the underfloor heating.
What happens after the heat exchanger?
After the heat has been transferred from outside into the apartment's circuit, the heat is passed on to the consumers, i.e. to the radiators. In modern apartments, radiators are usually not used and underfloor heating is used instead. The hot water for the shower, bathtub and washbasin is generated either by a heat exchanger or by a heat exchanger in combination with a heat storage unit, see diagram above.
How is energy or heat consumption measured in Germany?
In the past, up until around the 2000s, consumption was measured directly by measuring devices when radiators were used.
With the underfloor heating systems that are common today, the measurement is taken directly on the heat exchanger. In the picture you can see the white display control unit, which shows the energy consumption in kWh.
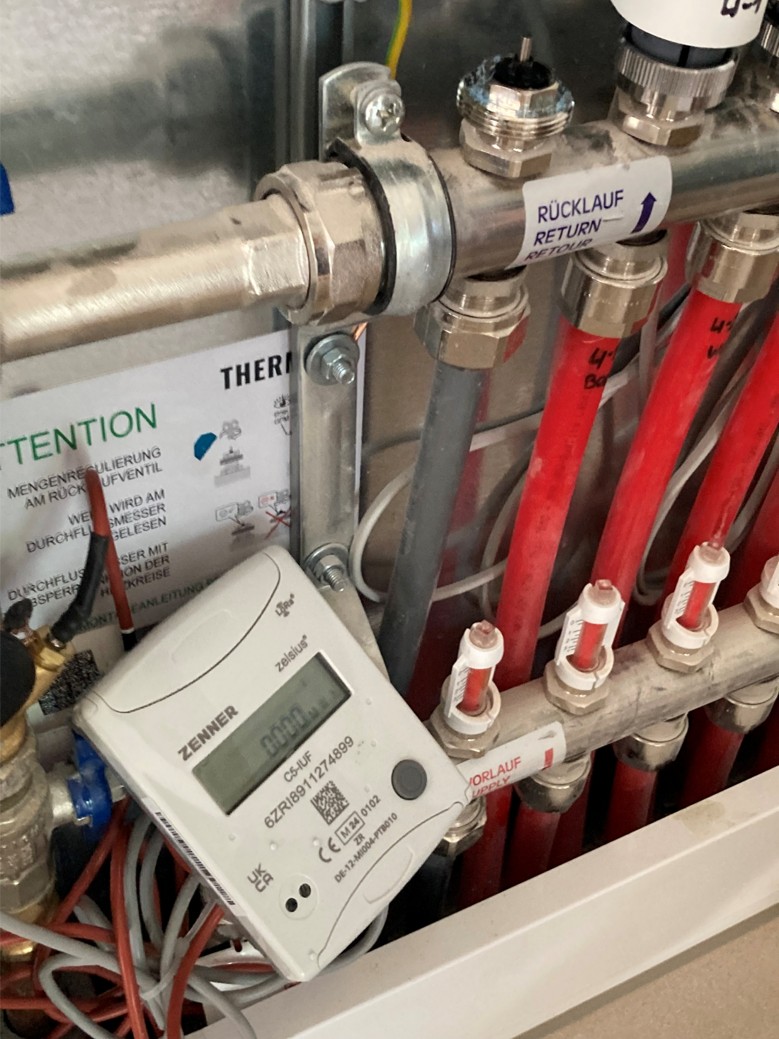
What is the disadvantage of measuring on the radiator?
It is difficult to determine whether the heat comes from the water from the heat exchanger, or whether the heat was generated by another heat source from outside. From outside it could be like the air/sun in the warm season or from another heat source, such as an additional heating system. Most radiator meters today are electronic, but there are still meters that show consumption by a small tube using the evaporation process. This kind of methodology is inaccurate therefore.
As a result of that, there is room for interpretation of the heat consumption and therefore there can sometimes be a dispute between the user (usually the tenant) and the heat generator (company or landlord).
In addition, the heating values are dimensionless and use only as an auxiliary measurement method. It is not possible to determine consumption directly. Only the conversion and interpretation by the metering service shows the proportionate consumption of an apartment in the total consumption of the building.

What is the advantage of measuring at the heat exchanger?
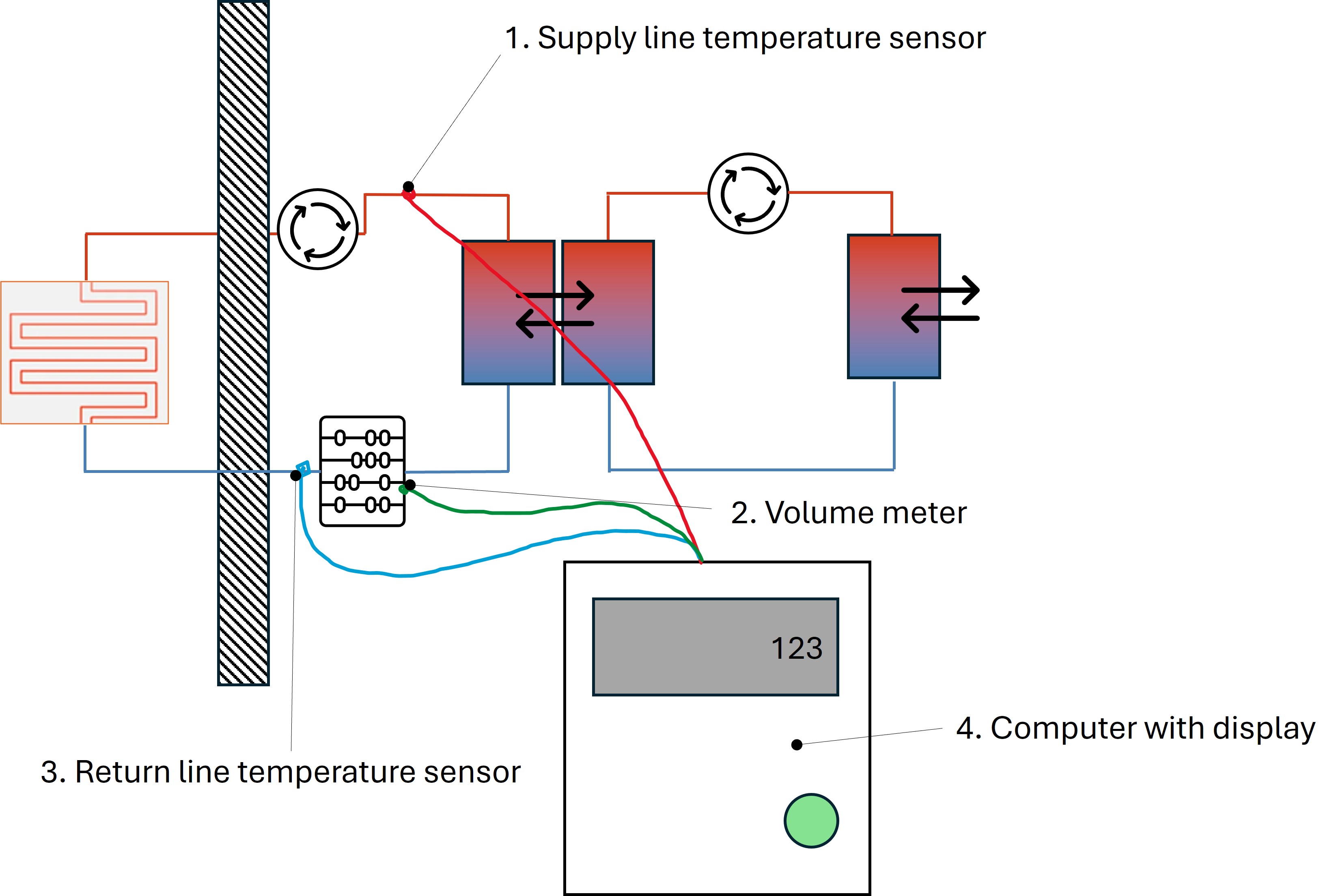
Since it is difficult to determine the consumed heat, which was actually produced by the heating system, the measure is taken directly at the heat exchanger in modern buildings.
The temperature of the water from the outside, the supply lines, to the heat exchanger is measured by a temperature sensor (1.). It is measured how much water flows through it by a volume sensor (2.). The temperature of the water in the return line is measured by another temperature sensor (3.) after it comes back from the heat exchanger.
In this way, the heat actually consumed can be determined very precisely. There is no room for interpretation here. The consumption determination is clear and is given directly in kWh.
Summary: What kind of heating systems are state of the art? How is energy/heating consumption measured? What does energy/heating consumption mean in Germany?
- Central and electric heating are the most used technologies
- generated heat is transported to the points of consumption
- Nowadays several closed heating circuits are used, which are connected to each other by heat exchangers
- Heat consumers are: underfloor-heating, radiators and warm water for bathtub, wash basin and shower
- The most accurate consumption is achieved via heat meters, because this shows the energy that is actually consumed in an apartment
Any open questions? Please contact us!